Taxes and Pay Stub Deductions
By Davis Clarkson , March 14 2025

Whenever you get your pay stub, there's a lot to pay attention to. You may notice a certain difference between the total pay and the money that gets to your account. This is the difference that contains information on various taxes and pay stub deductions.
These deductions don’t only determine where your money goes. This understanding is crucial for better budgeting and computation of taxes. You can also use it to check whether you are paying the right amount of taxes.
In this article, we will discuss the taxes and pay stub deductions. We'll guide you about various aspects of the pay stub. This is valuable for every worker during the tax season and throughout the year.
What Is a Pay Stub?
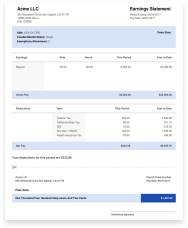
A pay stub is a document that is issued with the paycheck. It elaborates on the earnings and deductions that took place in a given pay period. This information is often documented in a paper document issued to the employee. It can also be in an electronic format.
Pay stubs give insights into how much you are paid. It also shows how the money is deducted before it is transferred to your bank.
That way, you can be certain that your employer deducts adequate taxes. You can also ascertain that any extra deductions you agreed to are processed correctly.
Essential Tax Information Found on Pay Stubs
Pay stubs are important since they contain significant tax information. This helps you determine your tax status. These are the main tax information that may be seen on the pay stubs:
Federal Income Tax Withholding
Federal income tax withholding is taken out of the employee’s salary. It is part of their pay that the employer pays the IRS on their behalf. This money is used to satisfy your federal income tax requirement for the year.
The amount to be withheld varies by the tax status of an individual. For example, this could be single, married filing jointly, or married filing separately. It also includes the number of allowances claimed on the W-4 form. This is among other factors. Income tax is progressive. Hence, the rates vary depending on the income you declare.
Your employer determines the amount with the help of tax tables. They also follow the percentage method as described under the IRS Publication 15-T. Therefore, you should revise your W-4 data once in a while. It's more necessary when any major change occurs. Examples include marriage, divorce, or having babies. This ensures the right amount of money is being withheld.
Social Security and Medicare Taxes
These are called FICA (Federal Insurance Contributions Act) taxes. The money collected will be used to finance some comprehensive Social Security. FICA taxes are not based on a system of progressive rates like federal income taxes. Instead, they are paid a certain percentage of your wages.
Social Security tax is usually 6.2% on your pay up to a certain limit. This implies that there may be a given m year you earn beyond this limit. You will not be taxed further on the remaining amount through Social Security tax.
Medicare tax is 1.45% on every earned income. It does not have a cap. There's an extra for those who earn more than $200,00. It's $250,000 for joint filers. They must pay an additional 0.9% Medicare tax on the amount that passes those limits.
These taxes average 7.65% of your income. Your employer will contribute the same amount, as well.
State and Local Taxes
Income tax deductions by state and at the local level are highly dependent on your tax code. It also depends on your place of employment. There are some states which have no income tax on the people. Examples are Florida, Texas, and Wyoming,
Some of them are progressive systems. The rate is higher depending on the income level. It could reach up to 13.3% in California and 10.9% in New York.
There is also additional income tax at the local level in some of the states. For instance, the general state tax rates in New York City are between 3.078% and 3.876%. Local taxes are also collected at the local municipality level. They could also be collected at the school district level. This depends on individual states.
Types of Payroll Deductions
There are different types of payroll deductions:
Mandatory Payroll Deductions
Some deductions are statutory, meaning they're prescribed by law. Federal income tax is the largest mandatory item for most employees.
FICA taxes, which are Social Security and Medicare taxes, are also statutory. They are aimed at funding retirement, disability, and hospital insurance.
State and local income taxes may be prescribed by your state's laws. They should be withheld, as well.
Wage garnishments can show up on the pay stub. That's if you are under a legal order to pay for some debts. It can also be child support or alimony, among others. Employers running companies are obliged to perform these deductions. That's when a court or government agency has ordered them to do so.
Voluntary Payroll Deductions
Voluntary deductions are those that the employer makes at the employee’s request. One is 401(k), 403(b), or other retirement savings plans provided by your employer. Employees can contribute up to $22,500 to these plans. An extra $7,500 catch-up contribution is allowed for employees who have reached the age of 50.
Health insurance premiums for medical, dental, and vision coverage are also voluntary. These are usually considerable deductions. However, they're valuable health insurance protections.
Health savings accounts (HSAs) are additional accounts that allow pre-tax contributions for qualified medical expenses, as are flexible spending accounts (FSAs).
Other expenses that may also be voluntary may include life insurance premiums. Disability insurance and supplementary insurance are other examples.
Other deductions may also be shown if an employee has authorized them. Examples are union dues and contributions to charity.
Pre-Tax vs. Post-Tax Deductions
This is another classification of deductions. Here, they are grouped according to the stage when they are made in calculating taxes.
Pre-tax deductions are made directly from the gross pay. That's before the computation of taxes; thus, it is a way of reducing the amount of taxes to be paid. Most of the pre-tax deductions are contributions to retirement plans. Others are insurance premiums and contributions to HSAs and FSAs.
A post-tax deduction is a form of deduction taken after tax has been determined in a given income. It differs from a pre-tax deduction as it does not change the taxable amount. These may include Roth 401(k) contributions and insurance premiums. It could also include deductions from wages due to legal actions.
Final Thoughts
When a pay stub is well-interpreted, you get a picture of your financial situation, including taxes. Taxes and pay stub deductions are important elements here.
It allows you to identify when you are being paid wrong. You can also determine whether the amounts that are being deducted are correct or not. This awareness helps in preventing nasty shocks when it comes to tax time.
Understanding your taxes and deductions helps with effective financial management. If you need to generate clear and accurate pay stubs, our pay stubs tool is for you. Easily create professional pay stubs that detail your earnings, taxes, and deductions. Take control of your payroll documentation today.
FAQs
Frequently Asked Questions
Similar Articles
We’ve helped numerous individuals and businesses create professional documents! Create yours today!